
LiDAR SERVICES

Lidar, or Light Detection and Ranging, is a remote sensing technology that uses pulsed lasers to measure distances to the Earth's surface. It creates detailed, three-dimensional representations of terrain and other features, providing valuable data for mapping, surveying, and analysis.
How Lidar Works:
-
Lidar systems emit laser pulses and measure the time it takes for the reflected pulses to return to the sensor.
-
By calculating the travel time, the distance to the surface is determined.
-
This process is repeated thousands of times per second, creating a dense point cloud of data representing the surface.
-
This point cloud can then be processed to generate various derivative products, such as Digital Elevation Models (DEMs) and Digital Surface Models (DSMs).
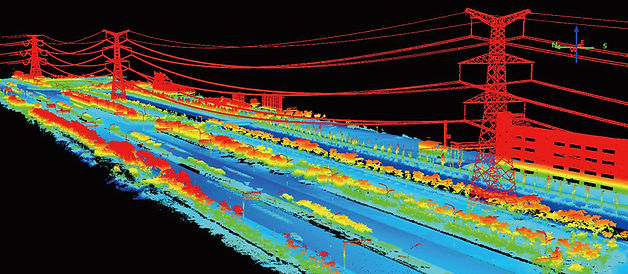
sUAS Aerial LiDAR Applications:
-
Lidar is used to create detailed elevation models of the Earth's surface, including bare earth and surfaces with vegetation and structures.
-
3D Digital Modeling: Both aerial and ground based SLAM LiDAR can be used to generate detailed 3D digital twins to asses infrastructure.
-
Lidar can be used to map the seabed and measure water depths in rivers, lakes, and oceans.
-
Lidar data can be used to assess forest structure, density, and canopy height, aiding in forest management.
-
Lidar has been used to reveal hidden archaeological features, including ancient cities and roads, obscured by vegetation or other features.
-
Lidar can be used to model urban areas, including buildings, infrastructure, and vegetation, aiding in urban planning and design.

